Situation Specific Arousal Analyzer (SSAA)
Human emotion involves experiential, behavioural, and physiological components, yet research in the humanities has often focused mainly on self-reported experiences. With the rise of wearable technology, real-time physiological data is now more accessible. The Empatica E4 wristband and the Situation Specific Arousal Analyzer (SSAA) app—available for OS X and Windows—enable non-clinical research into autonomic nervous system arousal, with a focus on state-specific anxiety in foreign language education. SSAA represents a methodological innovation, allowing researchers to link physiological data with affective variables like motivation, achievement, and willingness to communicate, bringing new depth to language learning anxiety research.
Trait anxiety is a stable aspect of personality linked to a predisposition for heightened arousal, while state anxiety is a temporary response to specific environmental triggers. This situational nature allows researchers to control and observe autonomic nervous system arousal through experimental design. However, within foreign language education, capturing real-time fluctuations in state-specific anxiety has been limited by methodological constraints. Advances in wearable technology, such as the Empatica E4 wristband, now offer access to physiological data, though its raw format presents challenges for educational researchers. To bridge this gap, the Situation Specific Arousal Analyzer (SSAA) was developed to make E4 data usable in foreign language research contexts. The SSAA enables the analysis of physiological indicators like heart rate variability and electrodermal activity under customizable conditions, expanding methodological possibilities and moving research beyond self-report measures.
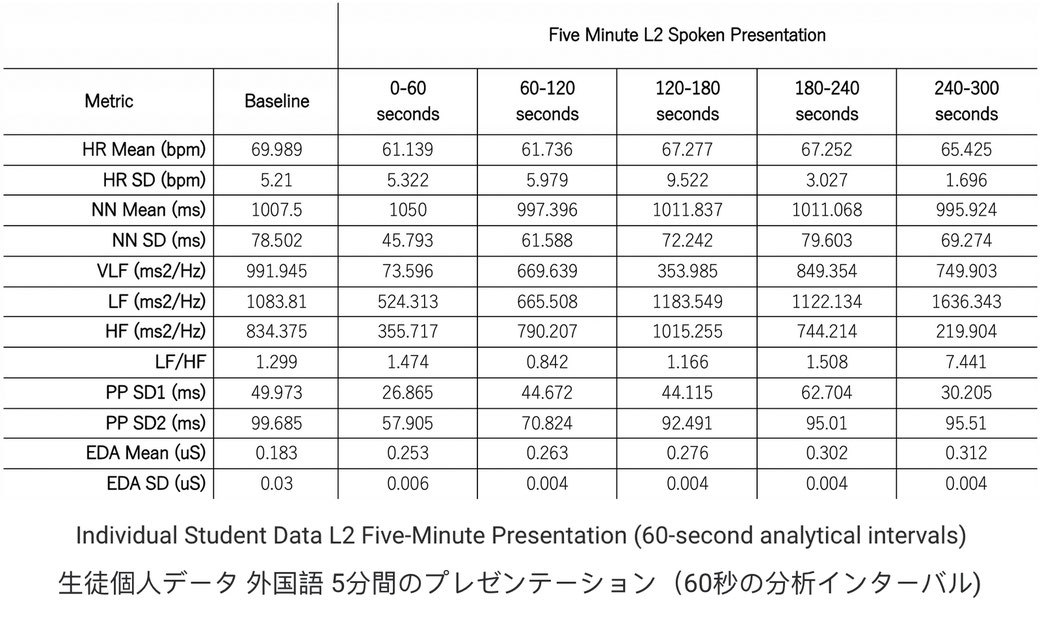
Using files exported from E4 Connect, the SSAA processes physiological data including Heart Rate (HR), Heart Rate Variability (HRV), and Electrodermal Activity (EDA) based on time intervals defined by the researcher. The interface supports both micro-level analysis—such as second-by-second changes during a spoken language task—and macro-level analysis across longer sessions like full classroom activities. For HR, the SSAA calculates mean (HRMean) and standard deviation (HRSD). HRV is analyzed across time-domain (e.g., NNMean, NNSD), frequency-domain (VLF, LF, HF, LF/HF ratio), and non-linear methods (SD1, SD2 via Poincaré Plots). EDA metrics include the mean (EDAMean) and standard deviation (EDASD), sampled as frequently as every 0.25 seconds. All results are exported as structured .csv files, along with visual outputs such as Lomb-Scargle Periodograms and Poincaré Plots, allowing for detailed, time-specific analysis of autonomic arousal.